Cracking the Roman Code: XLIX and the Secrets of 49
Ever wondered how to write 49 in those fancy Roman numerals you see on clocks, buildings, and Super Bowl logos? It's XLIX. But there's a whole lot more to this seemingly simple combination of letters than meets the eye. This isn't just about memorizing a sequence; it's about understanding a system that has endured for millennia. Join us on a journey through the intriguing world of Roman numerals and uncover the secrets behind representing 49.
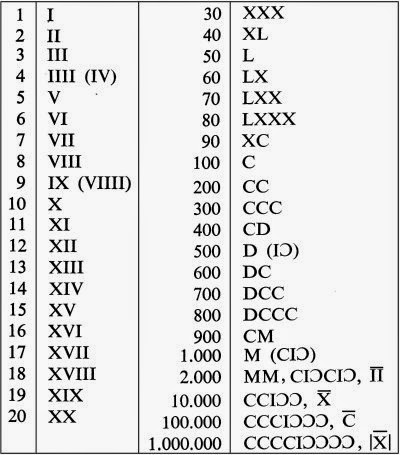
So, why is it XLIX and not IL? The Roman numeral system is based on addition and subtraction. While 'I' represents 1 and 'L' represents 50, placing the 'I' before the 'L' indicates subtraction. Therefore, XLIX translates to 50 - 10 + 9 = 49. Imagine trying to perform complex calculations using this system! Yet, it was the standard for centuries, shaping trade, architecture, and even how we mark time.
The origins of Roman numerals are shrouded in mystery, with theories ranging from Etruscan influence to tally marks carved on sticks. Regardless of their precise beginnings, these numerals became the backbone of numerical representation in the Roman Empire, facilitating everything from recording census data to inscribing dates on monuments. Their enduring legacy is a testament to their practicality and influence.
Representing 49, or any number for that matter, in Roman numerals carries a certain weight of history. It connects us to a time when numbers weren't just abstract symbols but tangible representations of value. Think about the copyright dates at the end of a movie – those Roman numerals add a touch of classic gravitas, a nod to a system that has stood the test of time.
Today, while we primarily use Arabic numerals for everyday calculations, Roman numerals remain relevant. They appear in everything from clock faces and chapter headings to regnal numbers of monarchs and Super Bowl editions. Understanding how to express numbers like 49 in Roman numerals allows us to appreciate these historical echoes in our modern world.
Converting 49 to Roman numerals involves understanding the subtractive principle. We know L is 50, and X is 10. Placing X before L signifies 50 - 10 = 40. Then, we add IX (9) to get 49. Therefore, 49 is represented as XLIX. Other examples include 4 (IV), 9 (IX), and 14 (XIV).
Three benefits of understanding Roman numerals include: 1. Historical Appreciation: It allows you to understand historical documents, inscriptions, and cultural artifacts. 2. Enhanced Number Sense: It provides a different perspective on numerical representation, deepening your understanding of numbers. 3. Cultural Literacy: Roman numerals are ubiquitous in our culture, from book chapters to building inscriptions. Knowing them allows you to fully engage with these cultural elements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Roman Numerals
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Aesthetically pleasing, classic feel | Cumbersome for complex calculations |
| Historically significant | Difficult to represent large numbers |
| Easy to represent small to medium numbers | No standardized representation of zero |
Five best practices for using Roman numerals: 1. Use uppercase letters: Roman numerals are traditionally written in uppercase. 2. Understand the subtractive principle: Remember that placing a smaller numeral before a larger one denotes subtraction. 3. Avoid repeating the same numeral more than three times consecutively: IIII is incorrect; IV is the correct representation of 4. 4. Use M for numbers greater than 1000: While extensions exist, M is the standard for 1000. 5. Be consistent: Use Roman numerals appropriately within a given context, maintaining a consistent style throughout.
Five real-world examples: 1. Super Bowl LVII (57). 2. King Charles III (the third). 3. Chapter headings in books (Chapter IV). 4. Clock faces (often using IIII instead of IV for four). 5. Copyright dates on movies.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Why is 49 XLIX and not IL? Because the subtractive principle applies to X and L, not I and L.
2. What is the largest number representable by standard Roman numerals? 3999 (MMMCMXCIX).
3. How do you write 99 in Roman numerals? XCIX
4. How do you write 1999 in Roman numerals? MCMXCIX
5. How do you write 2023 in Roman numerals? MMXXIII
6. Why do some clocks use IIII instead of IV? It's a matter of tradition and aesthetics, though the exact reason is debated.
7. Are lowercase Roman numerals ever used? Yes, sometimes for lower-level outlines or lists.
8. Where can I learn more about Roman numerals? Online resources, encyclopedias, and history books offer in-depth information.
Tips and tricks for remembering Roman numerals: Use mnemonics like "My Very Educated Mother Just Served Us Noodles" to remember the order of numerals (M, D, C, L, X, V, I). Practice converting numbers back and forth between Arabic and Roman numerals to solidify your understanding.
In conclusion, understanding how to write 49 in Roman numerals – XLIX – opens a window into a rich history of numerical representation. From the grandeur of the Roman Empire to the subtle details of a clock face, Roman numerals continue to resonate in our modern world. Knowing their meaning and usage enriches our cultural literacy and provides a deeper appreciation for the evolution of numbers. So the next time you see XLIX, remember it's not just a combination of letters, it's a connection to a fascinating past and a continuing legacy. This knowledge empowers you to decipher historical inscriptions, appreciate architectural details, and even impress your friends with your newfound numerical prowess. Explore the world of Roman numerals further, and discover the captivating stories they tell.
Unlocking fun your guide to getting the survey game
Conquer conversions your guide to the metric volume conversion calculator
Draft day gold unearthing the nfls best player available