Decoding the Elegance of RC Circuit Phasor Diagrams
Imagine a silent conversation between voltage and current, a subtle dance of lead and lag, all captured in the elegant geometry of a phasor diagram. This isn't abstract art; it's the visual language of resistor-capacitor (RC) circuits, a powerful tool for understanding how these fundamental components interact with alternating current.
RC circuits, the unsung heroes of electronics, form the backbone of countless applications, from simple filters to complex timing circuits. But their behavior under AC conditions can be perplexing without the right tools. Enter the phasor diagram, a graphical representation that transforms the complexities of sinusoidal voltages and currents into a clear, concise picture.
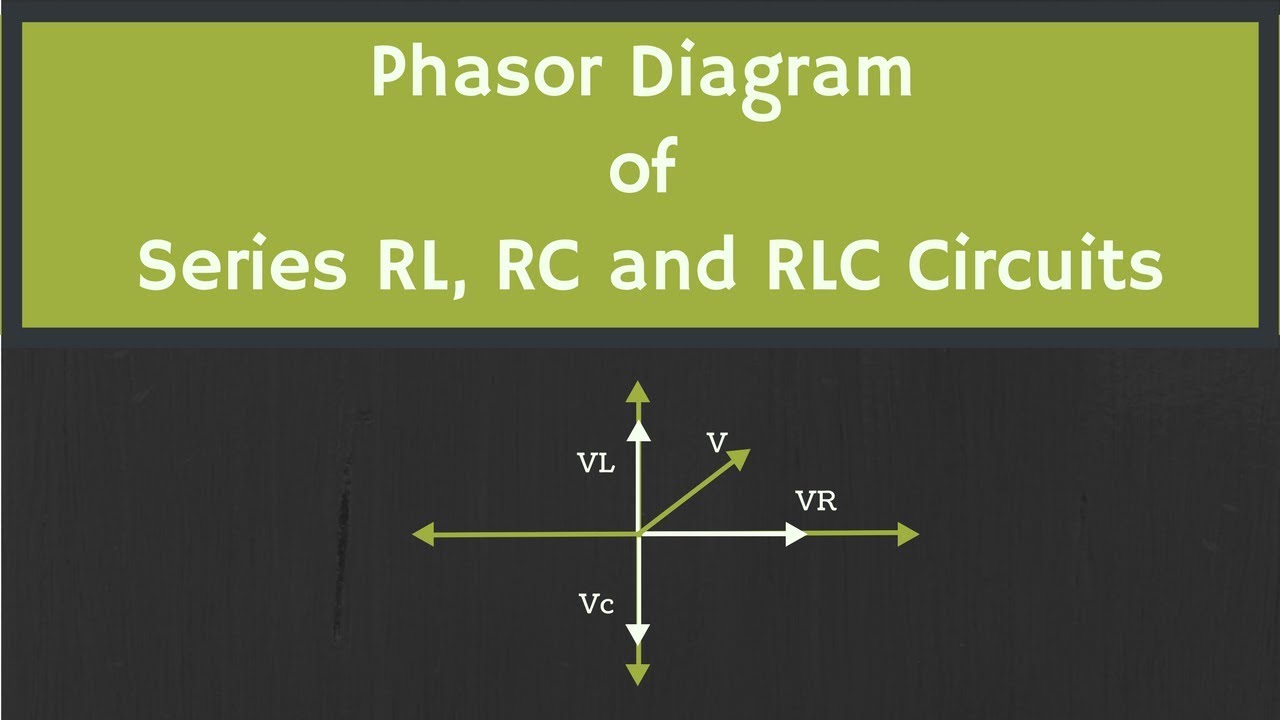
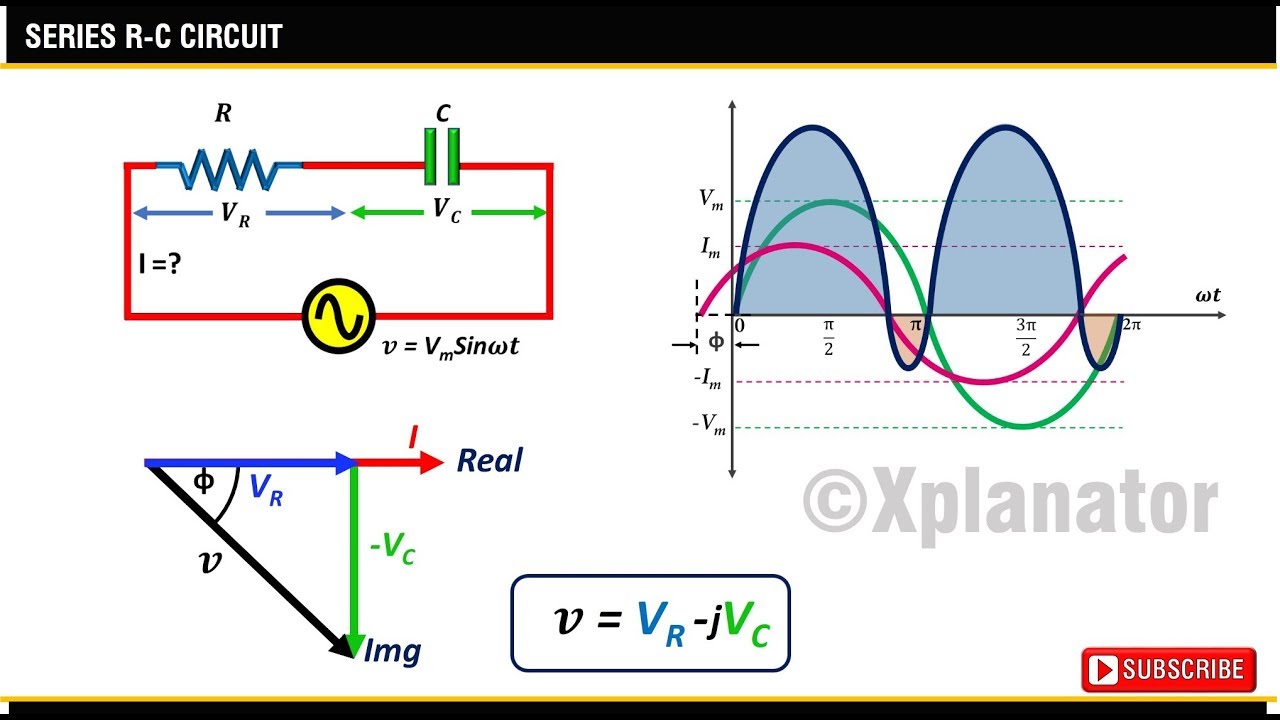
The essence of a phasor diagram lies in representing sinusoidal quantities as rotating vectors, or "phasors." The length of the phasor corresponds to the magnitude of the quantity, while its angle represents the phase shift relative to a reference. For RC circuits, this allows us to visualize the phase difference between the voltage across the resistor, the voltage across the capacitor, and the overall circuit current. This visual representation is crucial for understanding the overall circuit behavior.
Historically, the development of phasor diagrams went hand-in-hand with the understanding of AC circuit theory, pioneered by figures like Charles Proteus Steinmetz. His contributions in the late 19th and early 20th centuries laid the foundation for modern power systems analysis and emphasized the importance of visualizing AC quantities using phasor representations. This graphical approach became indispensable for analyzing complex circuits, including those with resistors and capacitors.
The significance of RC circuit phasor diagrams cannot be overstated. They offer a powerful method for analyzing circuit behavior, enabling engineers and technicians to predict voltage and current relationships, calculate impedance, and design circuits with specific frequency responses. Without phasor diagrams, understanding and designing even moderately complex AC circuits would be significantly more challenging.
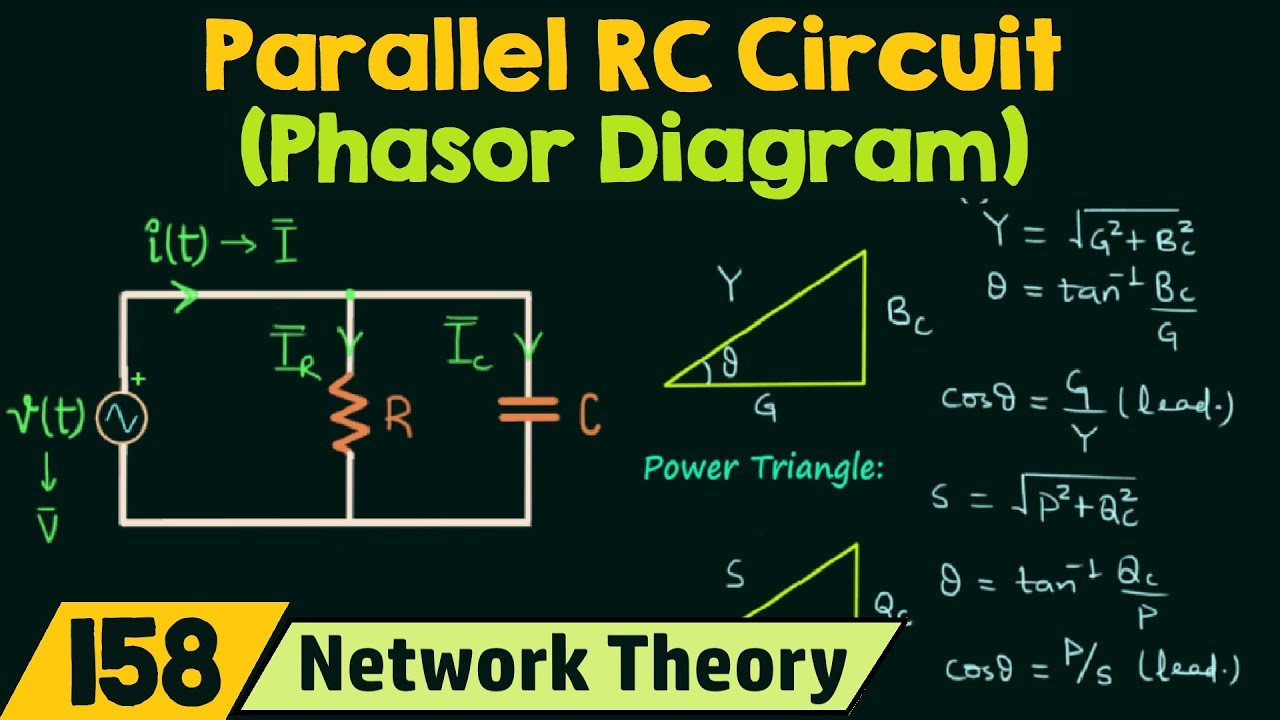
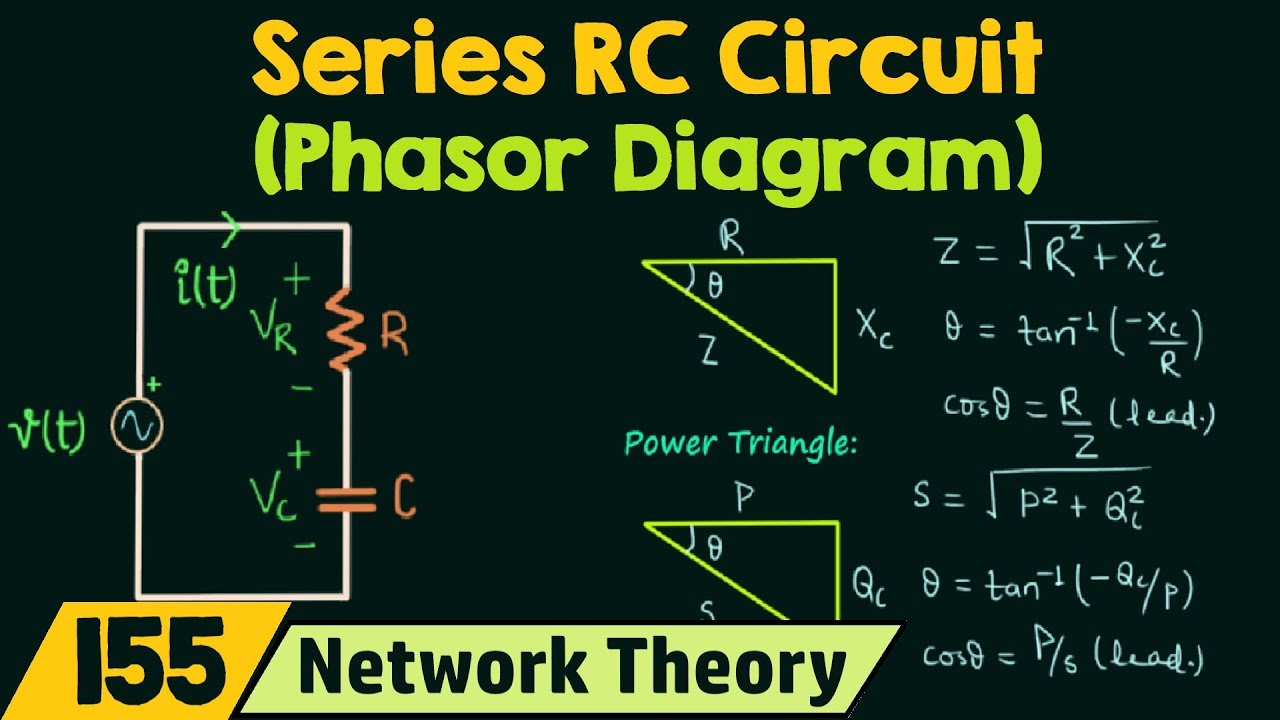
In an RC circuit, the voltage across the resistor is in phase with the current, while the voltage across the capacitor lags the current by 90 degrees. The phasor diagram captures this relationship, with the resistor voltage phasor aligned with the current phasor, and the capacitor voltage phasor lagging behind. The total circuit voltage is then the vector sum of these two phasors.
One benefit of using phasor diagrams is simplifying circuit calculations. Instead of dealing with complex differential equations, we can use simple vector addition and subtraction to determine voltage and current relationships. This visual approach allows for a more intuitive understanding of circuit behavior.
Another benefit is the ability to visualize the impact of frequency on circuit behavior. As frequency increases, the impedance of the capacitor decreases, leading to a smaller voltage drop across the capacitor and a larger current. The phasor diagram reflects this change, with the capacitor voltage phasor becoming shorter and the current phasor becoming longer.
Finally, phasor diagrams help in filter design. RC circuits are commonly used as low-pass or high-pass filters. By examining the phasor diagram, we can determine how the circuit will attenuate different frequencies, enabling the design of filters tailored to specific applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplifies complex AC circuit analysis | Only applicable to sinusoidal waveforms |
| Provides a visual representation of phase relationships | Can be challenging for complex circuits with multiple components |
| Facilitates circuit design and troubleshooting | Requires understanding of vector algebra |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a phasor? - A rotating vector representing a sinusoidal quantity.
2. Why does the capacitor voltage lag the current in an RC circuit? - Due to the charging and discharging behavior of the capacitor.
3. How is the total circuit impedance calculated in an RC circuit? - Using vector addition of the resistor and capacitor impedances.
4. What is the phase angle in an RC circuit? - The angle between the total voltage and the current.
5. How does frequency affect the phasor diagram? - Changes the length of the capacitor voltage phasor and the current phasor.
6. How are phasor diagrams used in filter design? - To visualize the attenuation of different frequencies.
7. What are the limitations of phasor diagrams? - Primarily applicable to sinusoidal waveforms and can be complex for intricate circuits.
8. Where can I learn more about phasor diagrams? - Textbooks on circuit analysis or online resources dedicated to electrical engineering concepts.
In conclusion, the phasor diagram for an RC circuit is more than just a graphical tool; it's a key that unlocks the intricacies of AC circuit behavior. Its ability to visually represent complex voltage-current relationships simplifies analysis, aids in circuit design, and empowers us to harness the full potential of these fundamental components. By mastering the language of phasors, we gain a deeper understanding of the elegant interplay between resistance, capacitance, and alternating current, enabling us to design and analyze circuits with greater precision and insight. This knowledge is essential for anyone working with electronics, from hobbyists to seasoned engineers. As technology advances and circuit complexity increases, the relevance of phasor diagrams remains steadfast, serving as a timeless tool in the ever-evolving landscape of electrical engineering.
Conquering the torque your jeep grand cherokees wheel security
Unlock the magic of words reading comprehension strategies for students
Navigating justice the role of the scott county tn criminal court clerk