Decoding the LCR Circuit Enigma: A Phasor Diagram Adventure
Ever feel like electrical circuits are speaking a secret language? Like you're at a party where everyone's fluent in resistor-capacitor-inductor chatter, and you're just nodding along, pretending to understand? Well, fret no more. Let's decipher the code with a surprisingly chic tool: the phasor diagram for LCR circuits. It's the key to unlocking the rhythmic dance of voltage and current in these complex electrical systems.
Imagine a circuit with a resistor, capacitor, and inductor all vying for attention. It's a bit like a complicated relationship – each component reacts differently to the alternating current. A phasor diagram provides a visual snapshot of these interactions, representing the voltage and current across each component as rotating vectors. This graphical representation makes it easier to grasp the phase relationships and overall circuit behavior.
Historically, understanding AC circuit behavior was a significant challenge before the introduction of phasor diagrams. Analyzing the sinusoidal variations of voltage and current was cumbersome, involving complex mathematical equations. The genius of phasor diagrams lies in their ability to simplify these calculations by representing AC quantities as static vectors, making analysis much more straightforward.
Phasor diagram analysis for LCR circuits is fundamental to electrical engineering. Its applications span various fields, from power systems to electronics design. Imagine designing a resonant circuit for a radio receiver - you'd need a phasor diagram to determine the component values that would allow you to select a specific frequency. Without this graphical tool, optimizing circuit performance for specific applications would be significantly more difficult.
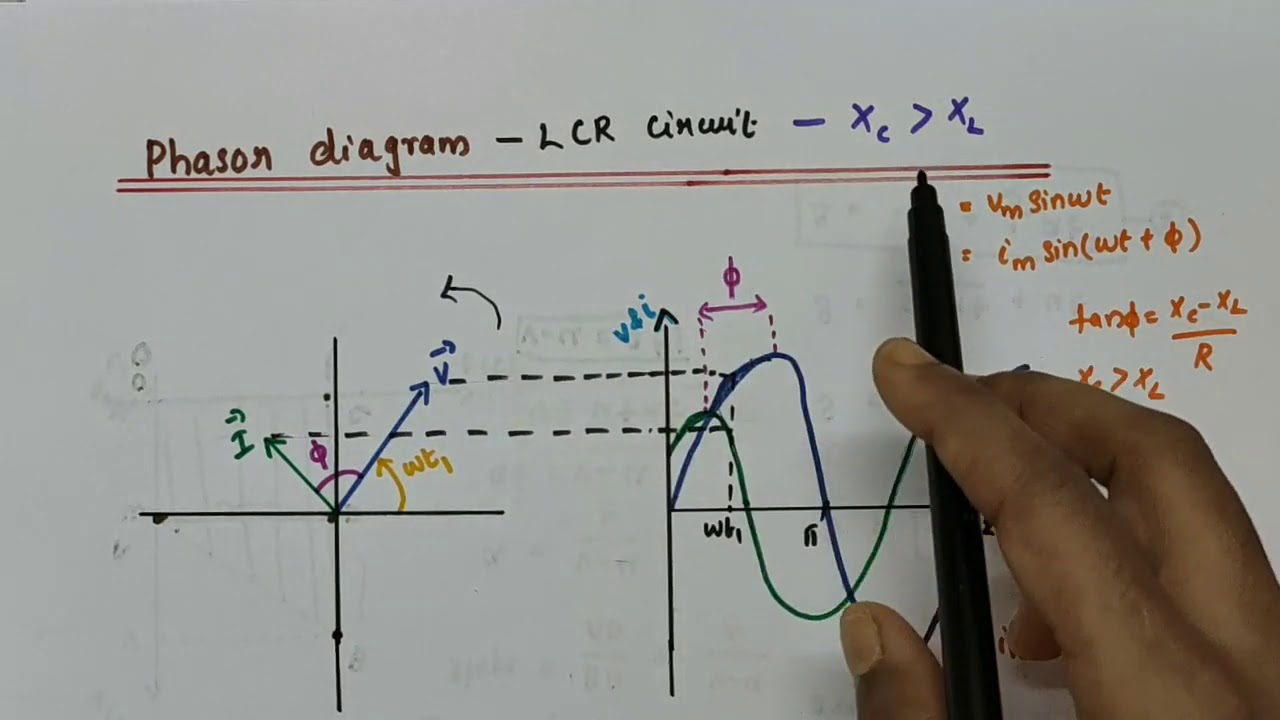
One of the main issues related to phasor diagrams is understanding the concept of phase difference. The voltage and current in an LCR circuit don’t always peak at the same time. This time lag is called the phase difference and is crucial in determining the overall circuit impedance. Phasor diagrams visually represent this phase difference, helping us understand its impact on the circuit's behavior.
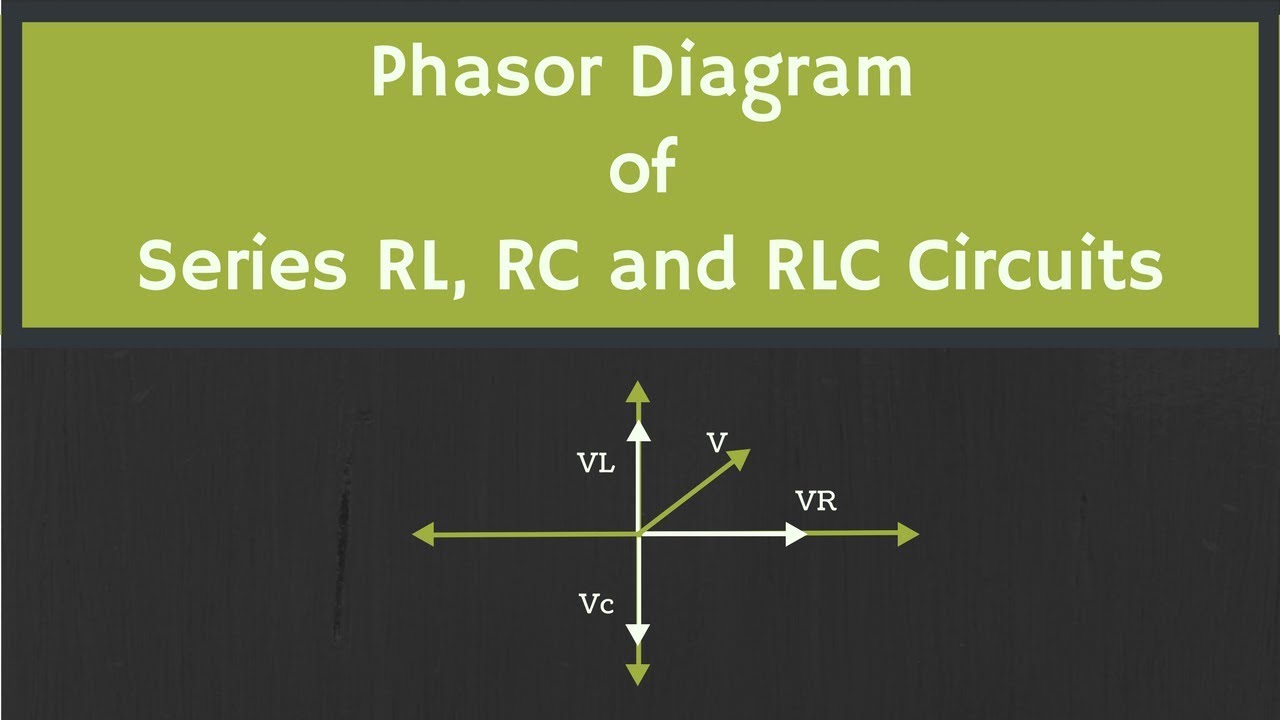
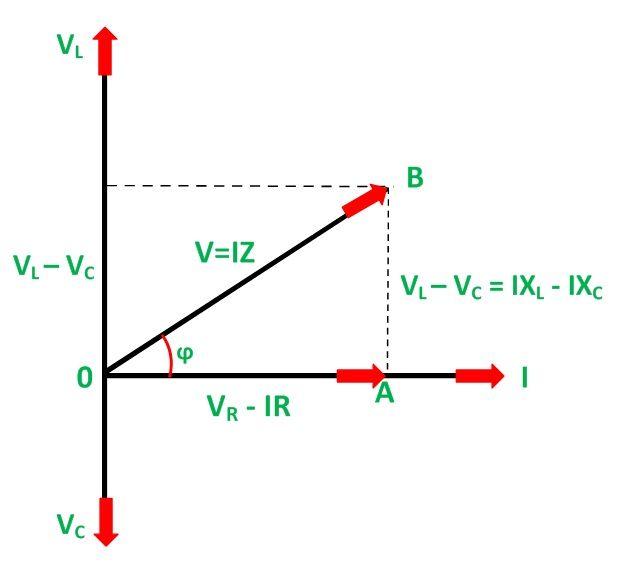
A phasor diagram uses vectors to represent the magnitude and phase of AC quantities. The length of the vector represents the magnitude, while its angle represents the phase relative to a reference. For instance, in a purely resistive circuit, the voltage and current are in phase, meaning their phasors point in the same direction. In a purely capacitive or inductive circuit, the phasors are 90 degrees apart, representing the phase difference between voltage and current.
Benefits of using phasor diagrams for LCR circuits abound. Firstly, they simplify the analysis of complex AC circuits, making it easier to visualize the interplay between voltage and current. Secondly, they help in understanding the concept of impedance, a measure of the overall opposition to current flow in an AC circuit. Finally, they are invaluable in determining resonance conditions, where the circuit's response to a particular frequency is maximized.
Creating a phasor diagram involves representing the voltage across each component (resistor, capacitor, and inductor) as rotating vectors. The vector sum of these individual voltage phasors gives the total voltage across the circuit. Similarly, the current phasor can be represented. The angle between the voltage and current phasors represents the phase difference.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplified AC circuit analysis | Can be challenging for complex circuits with multiple components |
| Visualization of phase relationships | Requires understanding of vector addition and subtraction |
| Impedance calculation | Doesn't directly provide transient analysis |
Best Practices for Phasor Diagrams: 1. Choose a suitable reference phasor. 2. Ensure accurate representation of magnitudes and phases. 3. Use clear labeling for each phasor. 4. Employ appropriate scaling for vector lengths. 5. Verify the diagram against circuit calculations.
FAQs: 1. What is a phasor? 2. Why are phasor diagrams useful? 3. How do you draw a phasor diagram for a series LCR circuit? 4. What is impedance? 5. What is resonance? 6. How is phase difference represented in a phasor diagram? 7. What are the limitations of phasor diagrams? 8. Where can I find more information on phasor diagrams?
Tips and Tricks: Remember to consider the frequency of the AC source when drawing a phasor diagram as it impacts the reactance of the capacitor and inductor. Utilize online resources and simulation tools to practice and visualize phasor diagrams.
In conclusion, phasor diagrams are an essential tool for anyone working with LCR circuits. They provide a powerful visual representation of complex AC circuit behavior, simplifying analysis and design. Understanding the concepts of phase difference, impedance, and resonance becomes significantly easier with the help of these diagrams. By mastering this elegant technique, you'll be well-equipped to navigate the intricacies of LCR circuits and unlock their full potential. Embracing the phasor diagram is like finding the perfect vintage accessory – it elevates your understanding of electrical circuits and empowers you to conquer even the most complex designs. So, ditch the confusion and embrace the clarity that phasor diagrams offer. You might just find yourself falling in love with electrical engineering. It's all about finding the right tools, and the phasor diagram? Well, that’s a must-have in your electrical toolkit.
The rise of voice shopping from lip gloss to groceries
Blast off your business sci fi store name generator
Decoding your noisy ac condensation pump