Decoding Your Power Cord: The Green, White, and Black Wire Trio
Ever wonder about the colored wires snaking out of your electrical appliances? They're not just random hues; they represent a carefully designed system ensuring the safe flow of electricity. This article delves into the world of power cords, specifically focusing on the roles of the green, white, and black wires – a trio vital for your safety and the proper functioning of your devices.
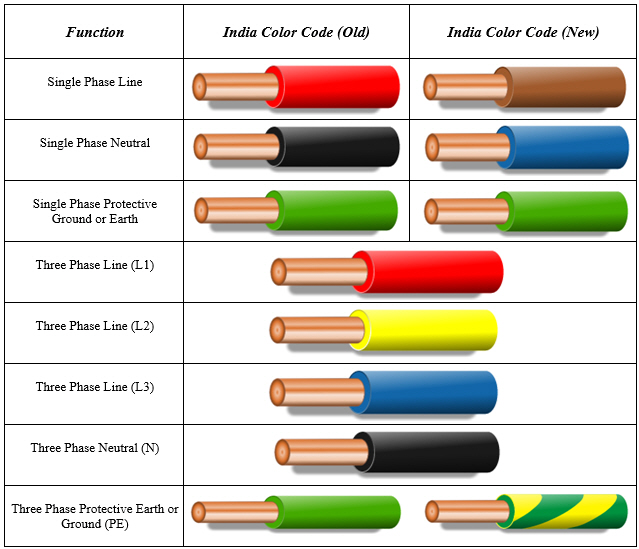
Understanding the purpose of each wire in a standard power cord is fundamental to electrical safety. The green wire, the guardian of your well-being, serves as the grounding wire. The white wire acts as the neutral conductor, completing the electrical circuit. And finally, the black wire carries the electrical current that powers your devices.
Miswiring these colored conductors can lead to dangerous consequences, including electrical shocks, short circuits, and even fires. Therefore, it's essential to grasp the significance of each wire's color and its corresponding function. This knowledge empowers you to identify potential hazards and ensures the safe operation of your electrical equipment.
While the color-coding system generally remains consistent, variations might exist depending on the specific application or regional regulations. Therefore, consulting local electrical codes and seeking professional advice when dealing with unfamiliar wiring configurations is always advisable.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the green, white, and black wires in a power cord, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding electrical safety in your home or workplace. We'll explore their individual functions, potential issues, best practices, and troubleshooting tips to empower you with the confidence to handle basic electrical tasks safely and effectively.
Historically, standardized color coding for electrical wires emerged to enhance safety and simplify electrical work. Initially, variations existed, leading to confusion and potential hazards. The adoption of a unified color code significantly reduced the risk of miswiring and improved the overall safety of electrical systems.
The green wire's role as the grounding conductor is paramount for safety. It provides a path for stray electrical currents to flow safely to the ground, preventing electric shocks. The white neutral wire completes the electrical circuit, allowing current to flow back to the source after powering a device. The black hot wire brings the electrical power to the appliance.
Proper grounding is essential to prevent electrical shocks. If a fault occurs within an appliance, the grounding wire directs the errant current to the ground, protecting the user from harm. Similarly, the neutral wire ensures a balanced electrical circuit, preventing voltage imbalances that could damage equipment.
One of the most common issues related to power cords is frayed or damaged insulation. This can expose the internal wires, creating a shock hazard. Another issue is loose connections, which can lead to overheating and potential fires.
Benefits of Correct Wiring:
1. Enhanced Safety: Correctly wired power cords minimize the risk of electrical shocks and fires.
2. Proper Device Function: Accurate wiring ensures that appliances receive the correct voltage and current, promoting optimal performance.
3. Increased Lifespan of Appliances: Proper wiring prevents voltage fluctuations that can damage electronic components, extending the lifespan of your devices.
Best Practices:
1. Regularly inspect power cords for damage: Replace frayed or damaged cords immediately.
2. Avoid overloading outlets: This can lead to overheating and fires.
3. Never remove the grounding pin: This compromises the safety mechanism of the grounding wire.
4. Consult a qualified electrician for complex wiring tasks: Don't attempt repairs beyond your skill level.
5. Use appropriate cord gauges for different appliances: Thicker gauge wires are necessary for high-power devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Understanding Power Cord Wiring
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased safety awareness | Requires time and effort to learn |
| Ability to troubleshoot minor electrical issues | Potential for overconfidence leading to unsafe practices |
FAQ:
1. What does the green wire do? It provides a grounding path for electrical faults.
2. What happens if the neutral wire is disconnected? The circuit will be incomplete, and the appliance won't function.
3. Can I use a power cord with a missing grounding pin? It's not recommended as it compromises safety.
4. What should I do if I see sparks from an outlet? Immediately turn off the power and call a qualified electrician.
5. What is the difference between a two-prong and three-prong plug? Three-prong plugs have a grounding pin for added safety.
6. How can I tell if a power cord is damaged? Look for frayed insulation, exposed wires, or loose connections.
7. Can I repair a damaged power cord myself? It's generally safer to replace a damaged cord.
8. Where can I find more information on electrical safety? Consult your local electrical code or reputable online resources.
In conclusion, understanding the function of the green, white, and black wires in your power cord is not just about technical knowledge; it's about ensuring your safety and the proper operation of your electrical devices. By following best practices, recognizing potential hazards, and seeking professional help when needed, you can create a safer electrical environment for yourself and those around you. Remember, electricity is a powerful force that demands respect and proper handling. Don't underestimate the importance of these seemingly simple colored wires – they play a vital role in keeping you safe from electrical hazards and ensuring the efficient functioning of your appliances. Take the time to educate yourself, and don't hesitate to call a qualified electrician if you have any doubts or concerns. Your safety is worth it.
Elevate your iphone 13 a guide to free wallpapers
Understanding poverty thresholds in the us
Mickey mouse and minnie mouse disneyland the ultimate guide