Navigating the New Energy Price Landscape
Remember those carefree days when we didn’t scrutinize our energy bills quite so intensely? It feels like a lifetime ago, doesn’t it? These days, the phrase "gas and electricity price cap" has become a common refrain in kitchen table conversations across the country. Understanding these fluctuations and how they impact our wallets is more crucial than ever.
The energy market can feel like a complicated beast, and keeping up with the latest changes can be daunting. But the truth is, understanding the basics of the new gas and electricity price cap can empower us to make informed decisions about our energy usage and potentially save some hard-earned cash. So, let's break it down and explore what this new price cap really means for us.
Essentially, the gas and electricity price cap sets a limit on how much energy suppliers can charge per unit of gas and electricity. It's designed to protect consumers from excessive price hikes, particularly for those on standard variable tariffs (SVTs). These tariffs are often the default option for many households, meaning the price cap has a direct impact on millions of people.
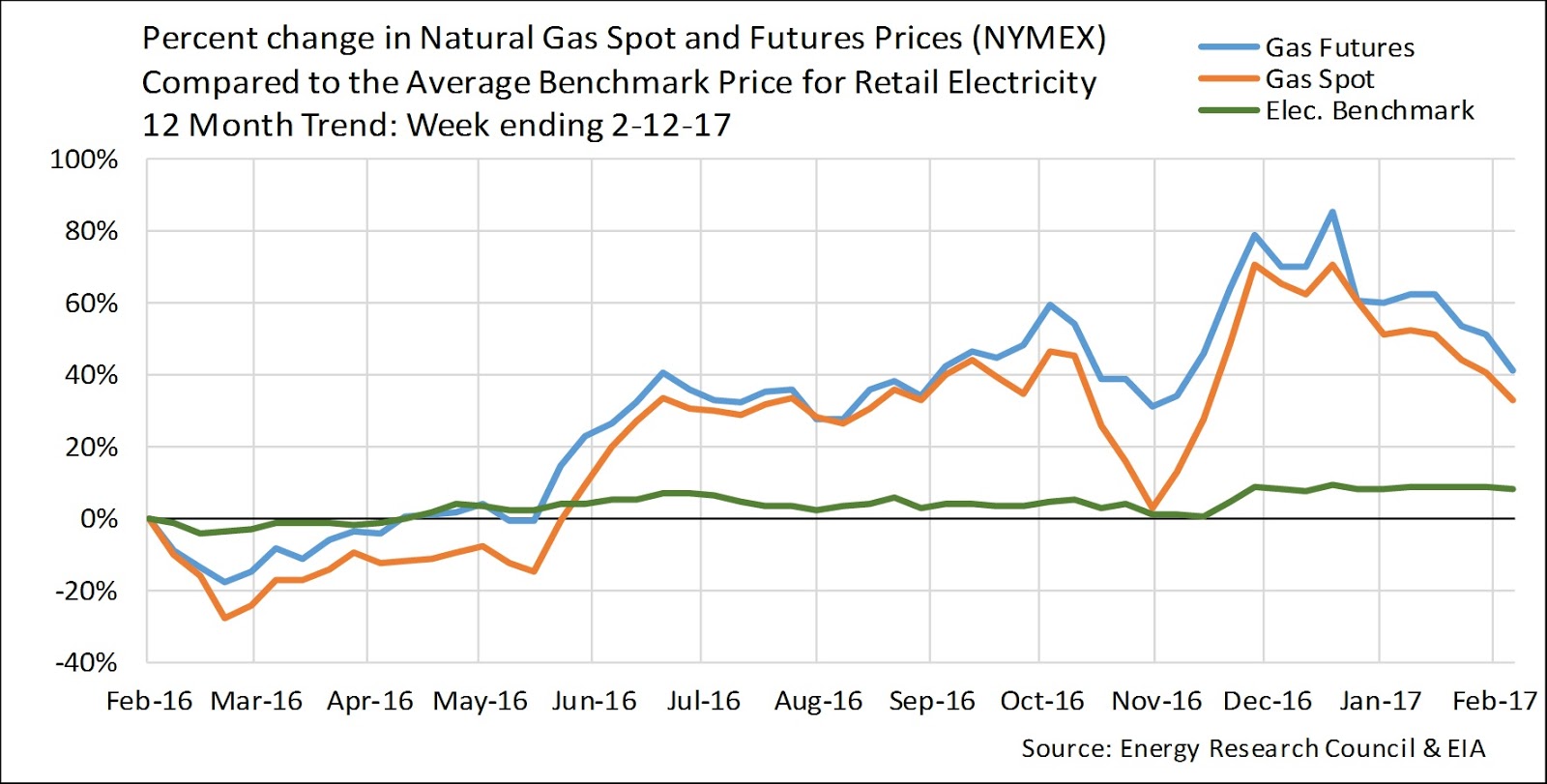
The price cap is usually reviewed and adjusted every three months by Ofgem, the energy regulator. This means the limit can go up or down depending on various factors, including wholesale energy prices, network costs, and operating costs for suppliers. Recent global events and market volatility have led to significant price cap increases, placing a strain on household budgets.
While the price cap offers a level of protection, it's important to remember it's not a fixed price for your entire energy bill. Your actual bill depends on how much energy you consume. So, even with the cap in place, reducing your energy consumption can still lead to lower bills. This brings us to the heart of the matter: How can we navigate this ever-changing energy landscape and make smart choices about our energy use?
Historically, energy prices have been subject to significant fluctuations. Before the introduction of the price cap, many consumers found themselves vulnerable to unpredictable price increases imposed by energy suppliers. The price cap was introduced to address this issue and provide a degree of stability and consumer protection in the energy market. It aims to ensure fair pricing and prevent suppliers from exploiting customers on default tariffs.
The main issues surrounding the price cap revolve around balancing consumer protection with the financial viability of energy suppliers. While protecting consumers from exorbitant prices is crucial, the cap must also allow suppliers to operate sustainably. Striking this balance is a complex challenge, particularly in times of market volatility.
One simple example of how the price cap works is to imagine a limit on the price of milk. If the price cap for milk is set at £1 per litre, no supermarket can charge more than that. However, they can still charge less. Similarly, the energy price cap sets a maximum price per unit of gas and electricity, but suppliers can offer tariffs below the cap.
While predicting the future of energy prices is akin to reading tea leaves, staying informed and proactive can empower us to make the best choices for our circumstances. Comparing tariffs, understanding our energy usage, and implementing energy-saving measures can help us navigate this evolving landscape and maintain some control over our energy bills.
Several websites offer valuable resources for comparing energy tariffs and understanding the price cap. These include comparison websites like Compare the Market and MoneySuperMarket, as well as the Ofgem website itself.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Energy Price Cap
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Protects consumers from excessive price hikes. | Doesn't guarantee the lowest possible prices. |
| Provides price stability and predictability. | Can discourage competition among suppliers. |
| Simplifies the tariff comparison process. | May not fully reflect the true cost of energy. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the energy price cap? A limit on the maximum price suppliers can charge for energy.
Who does the price cap protect? Primarily those on standard variable tariffs (SVTs).
How often is the price cap reviewed? Every three months.
Does the price cap guarantee the cheapest energy? No, it sets a maximum price, not a fixed price.
How can I save money on my energy bills? By reducing energy consumption and comparing tariffs.
Where can I find more information about the price cap? On the Ofgem website and comparison websites.
What factors influence the price cap? Wholesale energy costs, network costs, and supplier operating costs.
Will the price cap always exist? Its future is subject to ongoing review and debate.
In conclusion, navigating the intricacies of the new gas and electricity price cap can feel like a daunting task. However, understanding the basics empowers us to make informed decisions about our energy consumption and manage our household budgets effectively. By staying informed, comparing tariffs, and implementing energy-saving practices, we can navigate this complex landscape and maintain a sense of control over our energy expenses. The importance of understanding the price cap cannot be overstated, especially given the current economic climate. By being proactive and taking steps to manage our energy usage, we can not only reduce our bills but also contribute to a more sustainable energy future. While the road ahead may be uncertain, equipping ourselves with knowledge and practical strategies is the best way to navigate the ever-changing energy landscape and ensure we're getting the best possible deal.
Farrow ball dark green paint a rich sophisticated choice
Planning around tomorrows weather forecast
Snoopy images a guide to finding and using the beloved beagle