Power Up Your Adventures: Understanding Dual Battery Systems
Ever dreamt of powering a fridge in your car during a camping trip? Or running power tools without draining your starting battery? A two-battery setup in your vehicle can make these dreams a reality. This setup, often referred to as a dual battery kit or dual battery system, provides a separate power source for your accessories, leaving your primary battery dedicated to starting the engine.
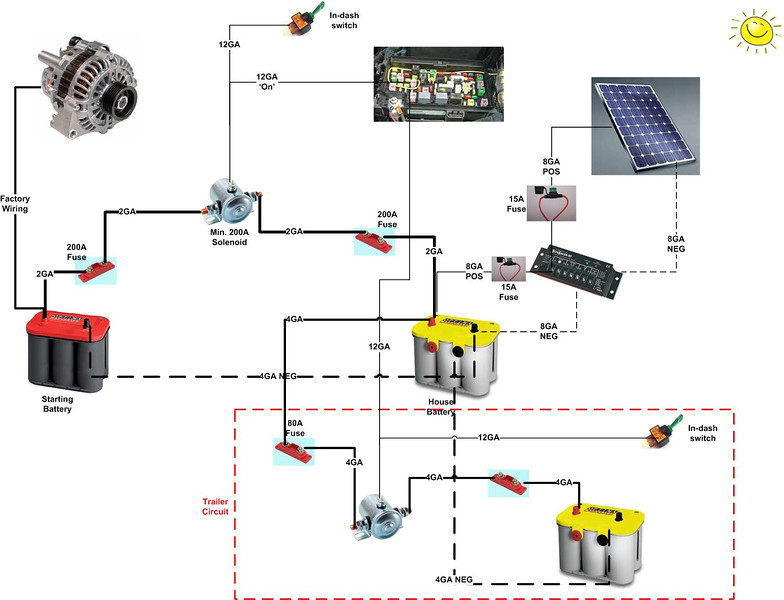
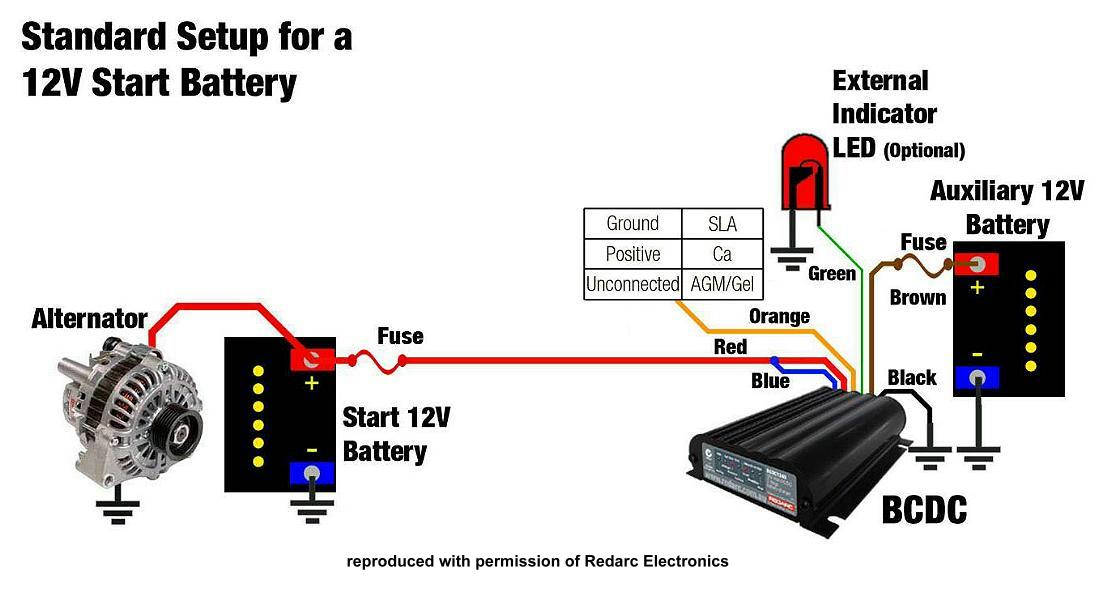
A dual battery system essentially involves installing a second battery, often a deep-cycle battery, alongside your vehicle's starting battery. These two power sources are connected via a battery isolator, a device that prevents the accessory battery from discharging the starting battery. This setup ensures that even if you power your accessories for extended periods, you'll still be able to start your engine.
The concept of supplementary battery systems for vehicles isn't entirely new. It has evolved from simpler setups used in RVs and boats to the more sophisticated dual battery kits we see today. Early implementations often involved manual switches to connect and disconnect the secondary battery. Modern systems utilize smart isolators or DC-to-DC chargers for more efficient charging and management of the two power sources.
The importance of a dual battery system becomes clear when you consider the increasing reliance on electronic devices and appliances in vehicles. From GPS navigation and dashcams to portable refrigerators and camping lights, the power demands on our vehicles are growing. A two-battery system ensures that you can power these accessories without the risk of draining your starting battery and being stranded.
One of the main issues associated with incorrectly installed dual battery systems is the potential for damage to the vehicle's electrical system. Using incorrect wiring or the wrong type of isolator can lead to overcharging or discharging of the batteries, potentially shortening their lifespan or even causing damage to the alternator. Proper installation by a qualified professional is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a two-battery setup.
A dual battery kit typically includes a secondary battery, an isolator or DC-to-DC charger, wiring, and mounting hardware. A deep-cycle battery is generally preferred for the secondary battery as it's designed to withstand repeated deep discharges, unlike a starting battery which is designed for short bursts of high current.
Benefits of installing a two-battery setup include: 1) Powering accessories without draining the starting battery, 2) Enhanced reliability for off-grid adventures, and 3) Enabling the use of power-hungry devices like inverters for AC power on the go. For example, you can run a camping fridge overnight without worrying about your car starting in the morning.
To install a dual battery system, you'll need to assess your power needs, choose the right components, and correctly connect them. Consulting a professional installer is recommended, especially for complex vehicle electrical systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dual Battery Systems
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Reliable power for accessories | Added cost and complexity |
| Extended off-grid capabilities | Requires space and weight in the vehicle |
| Prevents starting battery drain | Potential for installation errors |
Best practices for implementing a two-battery setup include using high-quality components, ensuring proper grounding, and regularly inspecting the system for any signs of wear or damage.
Real-world examples of dual battery system usage include powering camping equipment in overlanding vehicles, running power tools on work trucks, and providing reliable power for emergency services vehicles.
Challenges associated with two-battery setups might include difficulty finding suitable mounting locations, dealing with complex wiring, and ensuring compatibility with the vehicle's electrical system. Solutions often involve seeking advice from experienced installers and using specialized mounting brackets and wiring harnesses.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What type of battery should I use for my second battery? (Deep-cycle)
2. Can I install a dual battery kit myself? (Yes, but professional installation is recommended)
3. What is a battery isolator? (A device that prevents the auxiliary battery from discharging the starting battery.)
4. How much does a dual battery system cost? (Varies depending on components.)
5. What are the benefits of a DC-to-DC charger over a battery isolator? (More efficient charging.)
6. Can I run an inverter with a dual battery system? (Yes.)
7. How do I maintain my dual battery system? (Regular inspections and cleaning.)
8. What size second battery do I need? (Depends on your power needs.)
Tips and tricks for optimizing your two-battery setup include using a battery monitor to track the state of charge of both batteries and using energy-efficient appliances to minimize power consumption.
In conclusion, a dual battery kit is an invaluable upgrade for anyone who wants to enhance their vehicle's power capabilities. From powering essential equipment during emergencies to enabling extended off-grid adventures, the benefits of a dual battery system are numerous. While the installation process might seem daunting, with careful planning and execution, or by enlisting the help of a qualified professional, you can enjoy the peace of mind and freedom that comes with having a reliable and independent power source in your vehicle. Investing in a high-quality dual battery system is an investment in convenience, reliability, and the ability to fully explore and enjoy your passions, whether it's camping, overlanding, or simply having the power you need when you need it. Take the time to research your options, choose the right components, and install your system correctly to ensure years of trouble-free performance and unlock the full potential of your vehicle.
Whoosh how fast do skiers really fly downhill
Busted newspaper portsmouth ohio
Unlocking your cars potential the ultimate guide to mobile 1 oil filter cross referencing