Stair Handrail Regulations: Ensuring Safe Ascents and Descents
Imagine ascending a staircase, your hand reaching for a secure grip, only to find nothing but thin air. A seemingly simple oversight like a missing or improperly installed handrail can transform a routine action into a dangerous fall. This is why understanding and adhering to stair handrail building codes is paramount. These codes are not arbitrary restrictions, but rather carefully crafted guidelines designed to protect us from harm and ensure our safety on staircases.
Stair handrail regulations, often overlooked aspects of building design, are fundamental to safe navigation. These codes dictate critical aspects of handrail construction, including height, materials, and structural integrity. From private residences to public spaces, adhering to these regulations provides a vital layer of safety, mitigating the risk of falls and ensuring accessibility for everyone.
The history of stair handrail regulations is deeply intertwined with the evolution of building codes themselves. As structures became more complex and populations denser, the need for standardized safety measures grew. Early building codes, while rudimentary, recognized the importance of handrails in preventing falls. Over time, these regulations have evolved, becoming more refined and comprehensive to address the complexities of modern architecture and a greater understanding of human factors, such as ergonomics and accessibility.
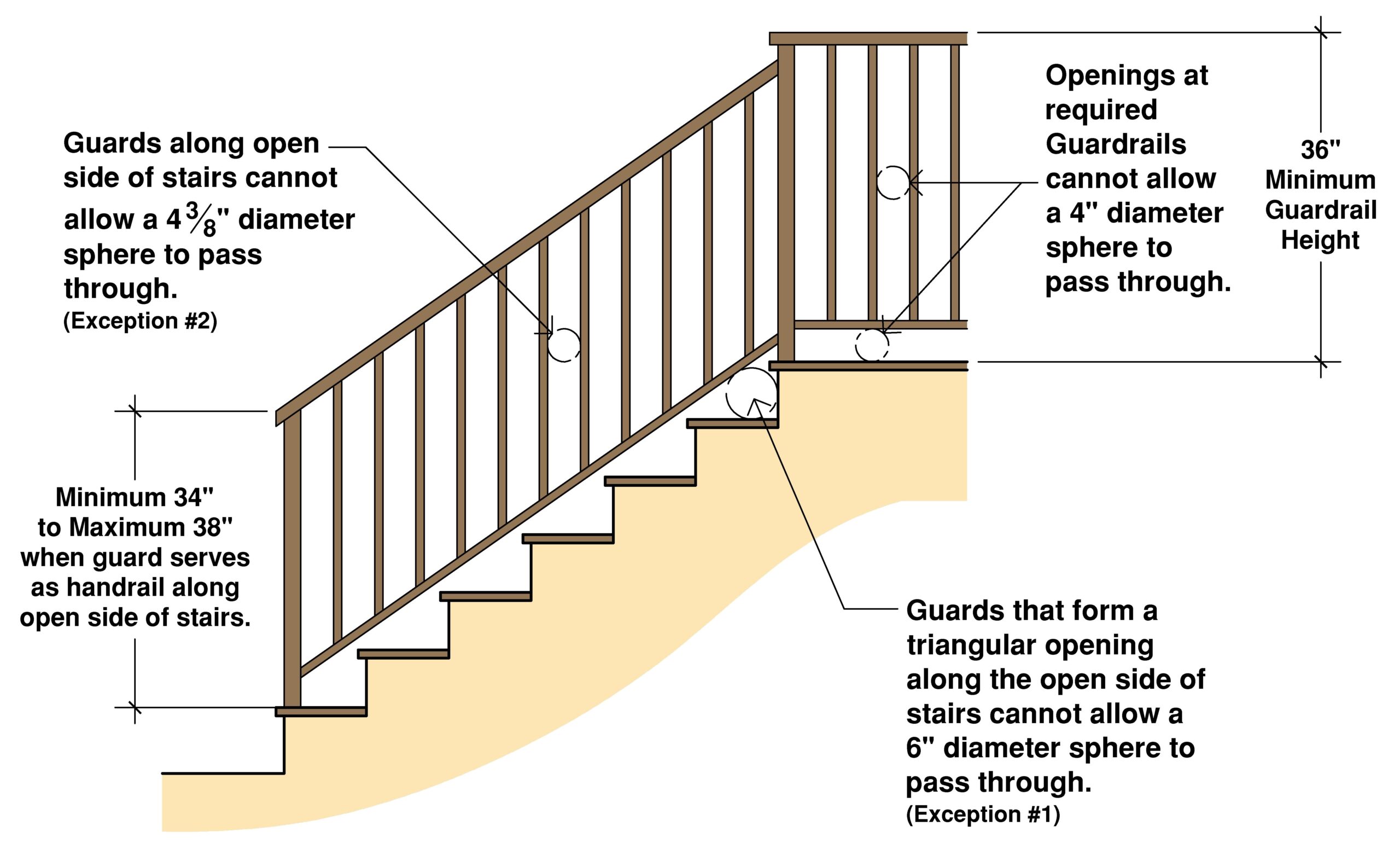
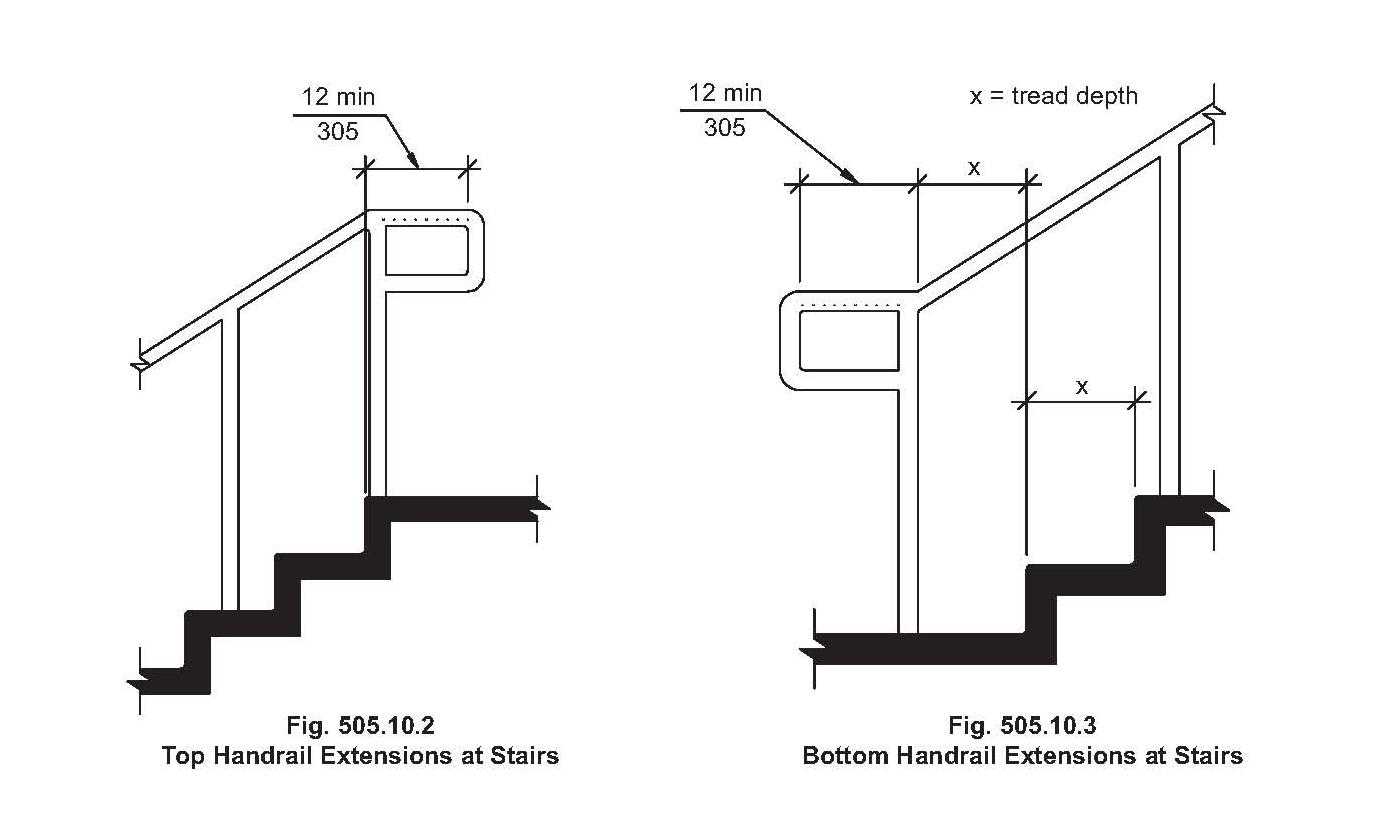
Handrail requirements are not uniform across the globe, varying based on local regulations and specific building types. However, the underlying principle remains consistent: to provide a stable and secure support for individuals navigating stairs. These stipulations typically encompass elements like handrail height, continuity, graspability, and load-bearing capacity. Understanding these specific requirements is vital for compliance and, more importantly, for ensuring a safe environment.
Failing to comply with stair handrail building codes can lead to serious consequences. Beyond the obvious safety risks, non-compliance can result in legal liabilities, costly renovations, and project delays. In commercial settings, it can lead to failed inspections and business closures. Therefore, ensuring compliance from the outset is not just a matter of following rules, but a crucial step in responsible construction and building management.
Handrail height is typically measured from the nosing of the stair tread to the top of the handrail. Most codes stipulate a height between 34 and 38 inches. Graspability refers to the ease with which a handrail can be gripped securely. This often translates into specific diameter requirements, typically between 1 1/4 and 2 inches.
Benefits of adhering to these codes include increased safety, improved accessibility for people with disabilities, and enhanced property value. For example, a properly installed handrail can prevent a fall, a continuous handrail provides uninterrupted support for those with mobility issues, and adherence to code demonstrates a commitment to safety that can increase a property’s marketability.
An action plan for implementing these regulations involves researching local building codes, selecting appropriate materials, engaging qualified professionals, and conducting thorough inspections. Successful implementation ensures long-term safety and peace of mind.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Strict Handrail Code Adherence
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased safety | Increased initial cost |
| Improved accessibility | Potential design limitations |
| Code compliance | Increased installation time |
Best practices include consulting with a structural engineer, using high-quality materials, ensuring proper installation, and conducting regular maintenance. These practices contribute to a safer and more durable handrail system.
Challenges in implementing these regulations may include navigating complex code requirements, sourcing specific materials, and managing project costs. However, overcoming these challenges is paramount to ensuring a safe and compliant staircase.
Frequently asked questions often revolve around handrail height, material specifications, and installation methods. Answers to these questions can usually be found in local building codes or by consulting with building inspectors.
Tips and tricks for complying with handrail regulations include using prefabricated handrail systems, consulting with experienced contractors, and keeping abreast of code updates.
In conclusion, stair handrail building codes are essential for ensuring safe and accessible staircases. Adhering to these regulations not only safeguards users from potential hazards but also enhances property value and demonstrates a commitment to responsible construction. While navigating these codes may present challenges, the benefits of compliance far outweigh the costs. From enhancing accessibility for all to mitigating the risk of serious injury, prioritizing stair handrail safety is an investment in the well-being of everyone who uses our stairs. Take the time to understand your local building codes and consult with professionals to ensure your staircases meet these vital safety standards. Your diligence will contribute to a safer environment for everyone.
The enduring mark of love tatuajes de la familia
Unlocking young minds fun and effective ejercicios de matematica para primer grado
Unlocking your potential indiana state employee handbook



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-final-CJ-01-157768d7ac40439da36f9ba69faa00c6.png)