Unlocking AC Circuit Secrets: The Power of Phasor Diagrams
Ever wondered how engineers tame the wild fluctuations of alternating current (AC)? The secret weapon? Phasor diagrams. These graphical wonders transform the intimidating realm of sinusoidal voltage and current waveforms into elegant, static vectors, making circuit analysis significantly less daunting.
Imagine trying to understand a complex dance routine by watching a sped-up video. Overwhelming, right? Phasor diagrams act like freeze-frames, capturing the essential information about the magnitude and phase relationship between voltage and current at a specific moment in time. This snapshot simplifies calculations and provides crucial insights into circuit behavior.
Phasor diagram analysis isn't just a theoretical exercise. It's a fundamental tool used in power systems, electronics, and telecommunications. From designing efficient power grids to optimizing signal processing in your smartphone, understanding voltage and current phasor relationships is paramount.
While the mathematical underpinnings of phasor diagrams might seem complex at first glance, the core concept is remarkably intuitive. By representing sinusoidal quantities as rotating vectors, we can visualize how voltage and current interact within a circuit, revealing key parameters like impedance, power factor, and resonance.
This exploration of voltage and current phasor diagrams will equip you with the knowledge to decipher AC circuit behavior. We'll delve into the history, practical applications, benefits, and even some challenges associated with this powerful analytical technique.
The concept of representing AC quantities with rotating vectors emerged in the late 19th century as engineers grappled with the complexities of AC power systems. Charles Proteus Steinmetz, a pioneering electrical engineer, is often credited with popularizing the use of phasor diagrams, which significantly simplified AC circuit analysis.
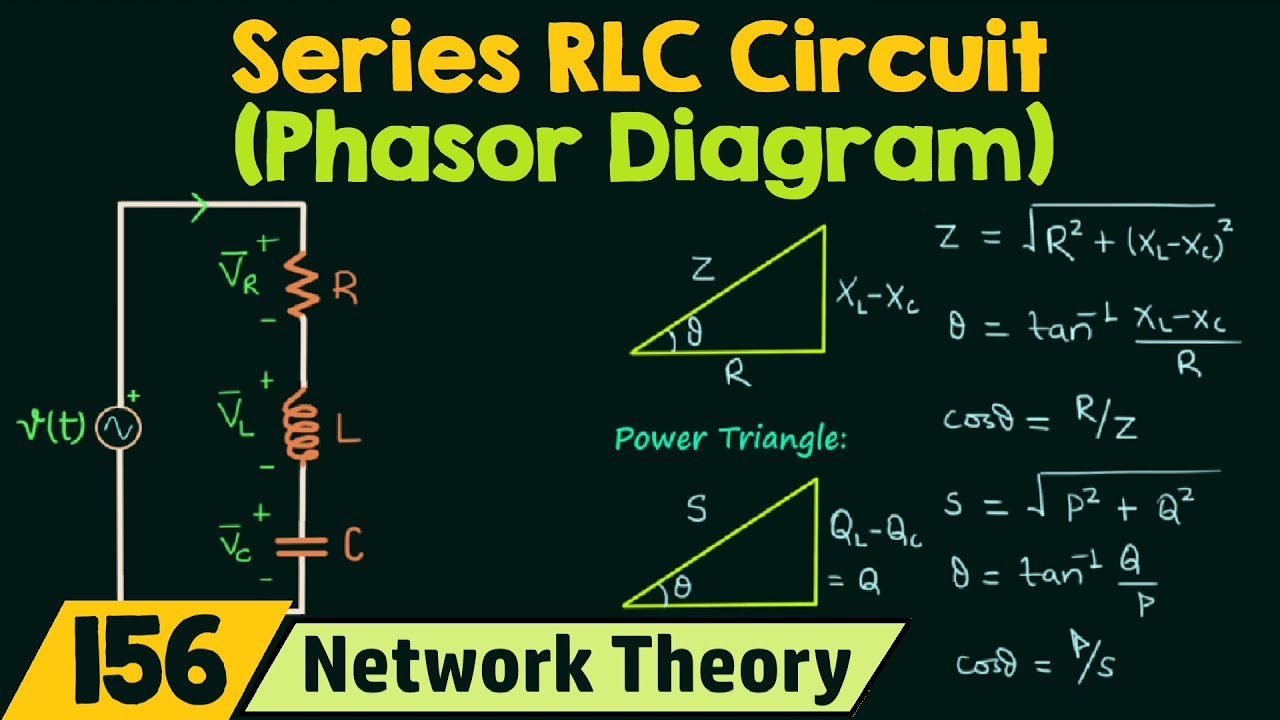
A phasor diagram is a graphical representation of AC voltages and currents as rotating vectors. The length of the vector represents the magnitude (peak value) of the quantity, while its angle relative to a reference axis represents the phase. This allows us to visualize the phase difference between voltage and current, which is crucial in AC circuit analysis.
Phasor diagrams offer numerous benefits. They simplify complex calculations, provide a clear visual representation of circuit behavior, and aid in understanding concepts like impedance and power factor. For example, in a purely resistive circuit, the voltage and current phasors are aligned, indicating zero phase difference. In a purely inductive circuit, the current phasor lags the voltage phasor by 90 degrees.
To construct a phasor diagram, identify the voltage and current waveforms in the circuit. Convert these sinusoidal functions into phasor representations, taking into account their magnitude and phase. Then, plot these phasors on a complex plane, using a common reference axis. The relative positions of the phasors reveal the phase relationship between voltage and current.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplifies AC circuit analysis | Primarily applicable to steady-state sinusoidal conditions |
| Visualizes phase relationships | Can become complex for highly intricate circuits |
| Facilitates understanding of impedance and power factor | Doesn't directly represent transient behavior |
Five best practices for using phasor diagrams include: 1) Clearly label all phasors, 2) Use a consistent reference axis, 3) Indicate the frequency of the AC signals, 4) Choose an appropriate scale for the phasor magnitudes, 5) Verify the results against other analysis methods when possible.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a phasor? A: A phasor is a complex number representing a sinusoidal function.
2. Why are phasor diagrams useful? A: They simplify AC circuit analysis by visualizing phase relationships.
3. How do I construct a phasor diagram? A: Represent sinusoidal quantities as rotating vectors and plot them on a complex plane.
4. What is the significance of the phase angle in a phasor diagram? A: It indicates the time difference between the peak values of voltage and current.
5. What is impedance in terms of phasor diagrams? A: Impedance is the ratio of voltage phasor to current phasor.
6. How does a phasor diagram represent a purely resistive circuit? A: The voltage and current phasors are aligned (zero phase difference).
7. How does a phasor diagram represent a purely inductive circuit? A: The current phasor lags the voltage phasor by 90 degrees.
8. What is the relationship between phasors and sinusoidal waveforms? A: Phasors represent the magnitude and phase of sinusoidal waveforms at a specific point in time.
Tips and Tricks: When dealing with complex circuits, break them down into simpler components and analyze each individually using phasor diagrams. Software tools can also be helpful for visualizing and manipulating phasors.
In conclusion, phasor diagrams are indispensable tools for understanding and analyzing AC circuits. Their ability to visually represent the complex interplay of voltage and current simplifies calculations, reveals key relationships, and facilitates deeper insights into circuit behavior. From power system design to electronic circuit analysis, mastering the art of phasor diagrams empowers engineers and technicians to tackle the challenges of the AC world. By embracing this powerful technique, we unlock a deeper understanding of the electrical systems that power our modern world. Explore online resources, textbooks, and software tools to further develop your skills in phasor analysis and unlock the full potential of this essential technique.
Finding solace loving memory poems for a fathers funeral
Wg step timing the secret sauce youve been missing
Unleash your inner kawaii the ultimate guide to cute aesthetic hello kitty pfps