Unlocking Fluency: Mastering the Past Simple of "Go"
Imagine yourself recounting a memorable trip, sharing anecdotes about your day, or simply describing your journey to work. In each of these scenarios, you'd inevitably find yourself reaching for the past tense, a fundamental building block of storytelling and everyday communication. Within this realm of past-tense constructions, the verb "go" takes on a unique form, often tripping up language learners. This exploration aims to demystify the past simple of "go," providing you with the tools to navigate this grammatical terrain with confidence.
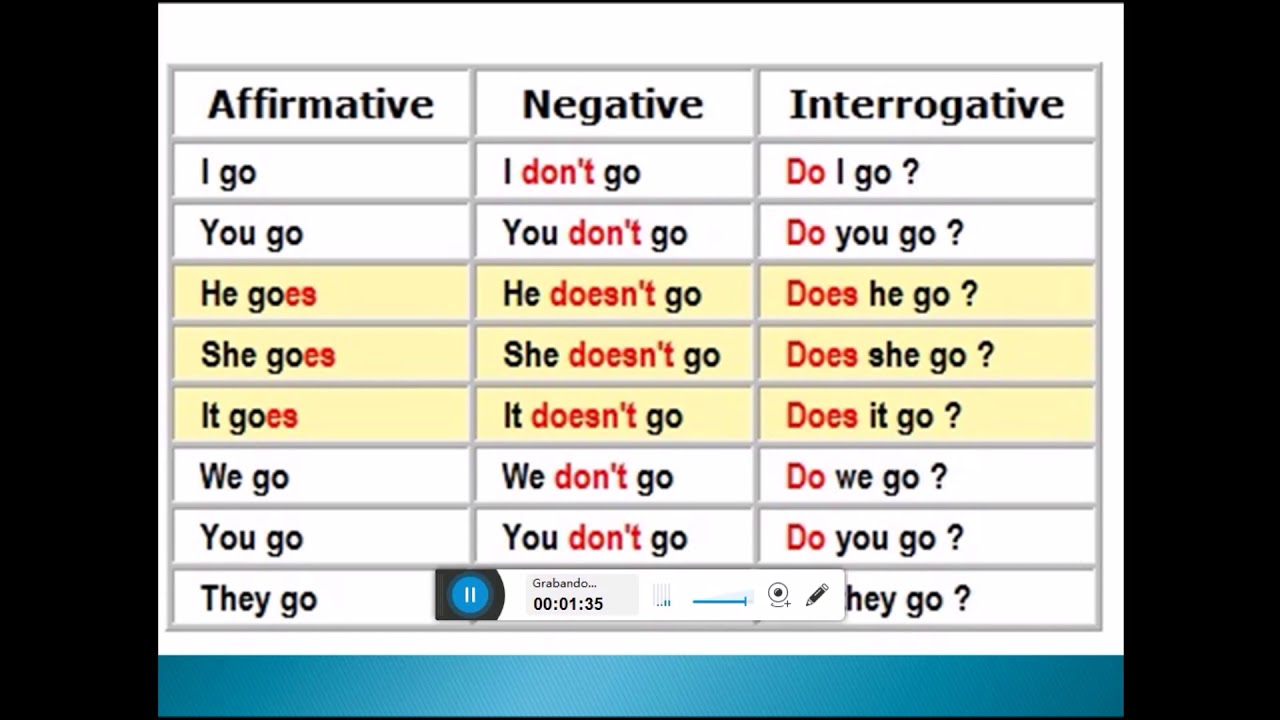
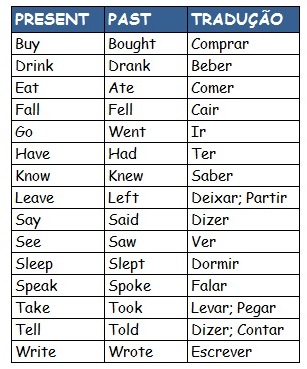
Unlike regular verbs that typically form their past tense by adding "-ed," "go" throws a curveball—its past simple form is "went." This irregular transformation is crucial to expressing that an action of movement or travel occurred in the past. Recognizing and correctly utilizing "went" is paramount for achieving grammatical accuracy and fluency in English.
Let's delve into the historical roots of this linguistic quirk. The irregular past form "went" has its origins in Old English, where the verb "wendan" was used to denote movement. As language evolved, "wendan" gradually gave way to "go" as the more common term for expressing movement. However, the past tense form "went," derived from "wendan," persisted, becoming ingrained in the English language's irregular verb patterns.
The significance of mastering the past simple of "go" extends far beyond merely acing grammar tests. It lies at the heart of effective communication, enabling you to express a wide range of actions and experiences that transpired in the past. Whether you're discussing a recent vacation ("We went to the beach yesterday") or narrating a historical event ("The explorers went on a perilous journey"), using "went" correctly ensures clarity and precision in your language.
However, the seemingly simple swap of "go" to "went" can often lead to common errors. One frequent pitfall is the incorrect use of "goed" as the past tense of "go." This mistake stems from the tendency to apply the regular "-ed" past tense ending to irregular verbs. Another stumbling block arises when speakers fail to recognize the irregular nature of "go" and incorrectly use the present tense form ("go") when referring to past events. Overcoming these challenges involves consistent practice, exposure to correct usage, and a firm grasp of irregular verb forms.
To solidify your understanding, let's examine a few illustrative examples:
Correct: She went to the library after school.
Incorrect: She goed to the library after school.
Correct: They went on a hike last weekend.
Incorrect: They go on a hike last weekend.
By paying close attention to the correct usage of "went" in these examples, you can begin to internalize its form and function in various contexts. Consistent practice and a conscious effort to incorporate "went" accurately in your speaking and writing will pave the way toward mastering this fundamental aspect of English grammar.
In conclusion, while the past simple of "go" might initially appear as a minor grammatical detail, its impact on fluency and clarity of expression is significant. By acknowledging its irregular form—"went"—and committing it to memory, you unlock the ability to recount past experiences, share stories, and engage in conversations about the past with accuracy and confidence. As you continue your journey toward English language proficiency, remember that even seemingly small grammatical nuances, when mastered, contribute significantly to your overall communicative prowess.
Cross century fountain pen a comprehensive review
Remembering mary lou murphy a life celebrated
The sweet simplicity of gorditas de azucar caseras a recipe to savor