Unlocking Math: Exploring Tools for Addition and Subtraction
Mathematics, a fundamental pillar of education and daily life, can sometimes present challenges, especially in the foundational concepts of addition and subtraction. Fortunately, a range of tools exists to support learners of all ages in mastering these essential skills. This article delves into the world of math aids for addition and subtraction, exploring their history, benefits, and practical applications.
From the earliest days of counting on fingers to the development of sophisticated digital tools, humans have sought ways to simplify and enhance mathematical calculations. The abacus, a timeless calculating tool, stands as a testament to our enduring quest for numerical mastery. These aids, in their various forms, serve as bridges to understanding, helping learners visualize and internalize the principles of addition and subtraction.
The importance of mastering addition and subtraction cannot be overstated. These operations form the bedrock for more complex mathematical concepts, including multiplication, division, algebra, and calculus. A strong foundation in these fundamental skills empowers learners to confidently navigate higher-level mathematics and apply them to real-world situations.
However, using math aids effectively requires thoughtful consideration. Over-reliance on tools can sometimes hinder the development of mental math skills. The key lies in striking a balance, utilizing these aids as stepping stones towards independent calculation abilities.
Understanding how to choose and apply the right tool for the task is crucial. Whether it's a simple number line, colorful counters, or a digital application, each tool offers unique advantages. The goal is to select the aid that best suits the learner's needs and learning style, promoting a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical concepts.
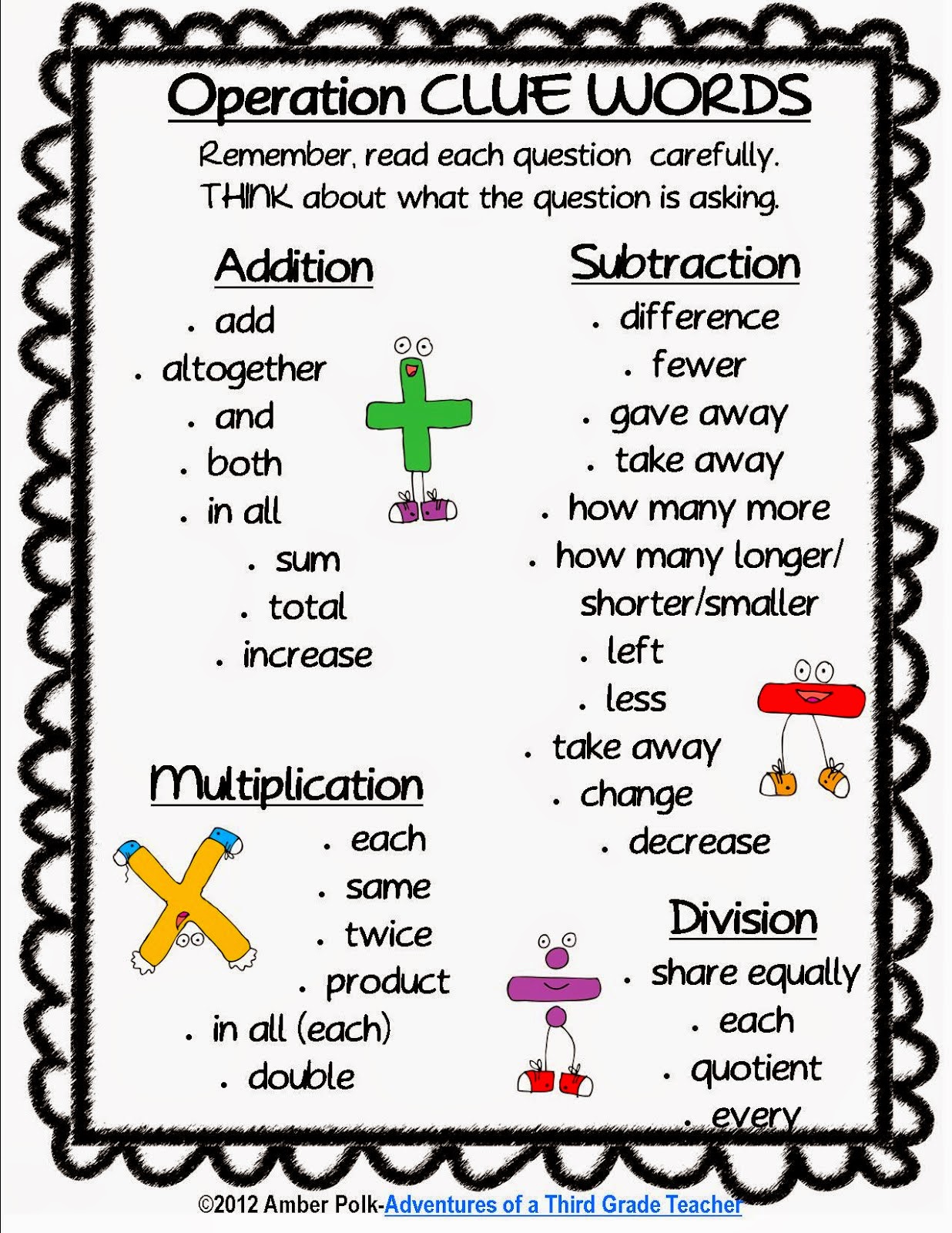
Definitions are important in understanding these aids. Addition is the process of combining two or more numbers to find their total, while subtraction involves taking one number away from another to find the difference. A simple example of addition is 2 + 3 = 5. For subtraction, 5 - 3 = 2.
Benefits of using math aids include improved number sense, enhanced visualization of mathematical concepts, and increased confidence in tackling numerical problems. For example, using blocks can visually demonstrate the concept of adding 3 + 2, leading to a better grasp of the concept.
Creating an action plan for using math aids might involve starting with concrete objects like counters, progressing to visual aids like number lines, and eventually transitioning to more abstract tools like calculators for complex calculations. A successful example would be a student initially struggling with addition gaining proficiency and confidence after using counters and gradually moving towards mental math.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Math Aids
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Visual and hands-on learning | Potential over-reliance |
| Improved understanding of concepts | Can hinder mental math development |
| Increased confidence | May not be suitable for all learners |
Best Practices for Implementing Math Aids:
1. Start with concrete materials: Begin with manipulatives like counters or blocks.
2. Gradually transition to visual aids: Move to number lines or charts.
3. Connect to real-world examples: Use scenarios like shopping or sharing toys.
4. Encourage mental math alongside aid use: Practice mental calculations regularly.
5. Personalize aid selection: Choose tools based on individual learning styles.Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the best math aids for beginners? - Simple counters and number lines are ideal.
2. How can I prevent over-reliance on math aids? - Balance aid use with mental math practice.
3. Are digital math aids effective? - Yes, when used appropriately and in moderation.
4. Can math aids be used for older students? - Yes, for complex calculations or visualizing abstract concepts.
5. How can I incorporate math aids into everyday learning? - Use them during games, cooking, or other activities.
6. What are some examples of advanced math aids? - Graphing calculators, specialized software.
7. How do I choose the right math aid? - Consider the learner's age, learning style, and specific needs.
8. Where can I find reliable math aids resources? - Educational websites, teacher supply stores, libraries.
In conclusion, math aids for addition and subtraction serve as invaluable tools in the journey of mathematical learning. From concrete manipulatives to digital applications, these aids offer diverse approaches to understanding and mastering these fundamental operations. By thoughtfully integrating these tools into educational practices and daily activities, we can empower learners to build a solid mathematical foundation, paving the way for future success in STEM fields and beyond. It's important to remember that the effective use of these aids lies in balancing their application with the development of mental math skills. Encourage learners to gradually transition from concrete tools to more abstract methods, fostering a deep understanding of mathematical concepts and promoting a lifelong love of learning. Explore the variety of math aids available, experiment with different approaches, and witness the transformative power of these tools in unlocking mathematical potential. Embark on this journey of discovery and empower yourself or your learners to conquer the world of numbers with confidence and enthusiasm.
Decoding the art of subtle flirtation
Matching bathroom tiles shower and floor debate
Taming your hvac duct insulation decoded