Unlocking Music Literacy: Understanding Note Names and Their Significance
Imagine trying to read a book without knowing the alphabet. That's what it's like trying to understand music without knowing the names of the notes. Just like letters form words and sentences, musical notes are the building blocks of melodies, harmonies, and entire compositions.
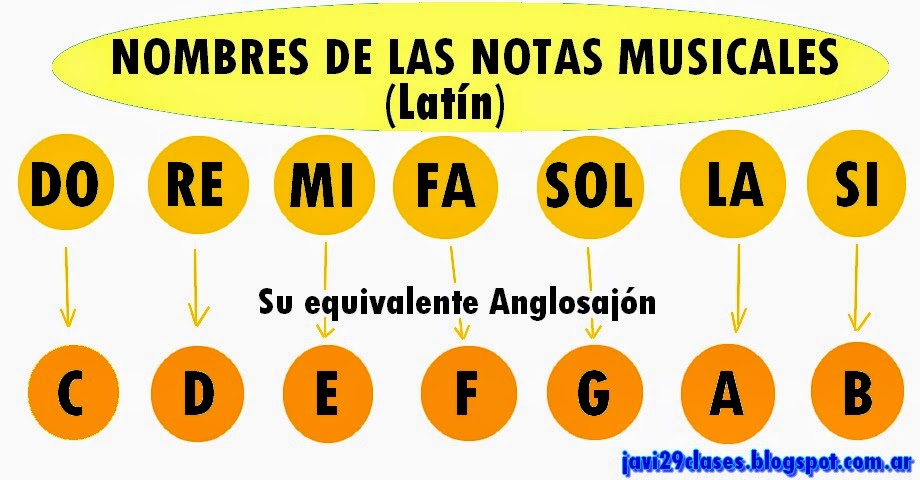
In the realm of Western music, we primarily use a system of seven letter names to represent these musical building blocks. These seven letters – A, B, C, D, E, F, and G – are repeated across the musical spectrum, creating a framework for understanding pitch and melody. Each note represents a specific frequency or pitch, and when combined in various sequences and rhythms, they create the music we know and love.
The history of these letter names can be traced back to ancient Greece and the influence of philosophers like Pythagoras. They saw a connection between music and mathematics, attributing specific ratios and intervals to different notes. This system evolved over time, incorporating influences from various cultures and musical traditions, ultimately leading to the system we use today.
Understanding note names is paramount for anyone who wants to delve deeper into the world of music. Musicians, composers, and even casual listeners benefit from this knowledge. It's the key to reading sheet music, transcribing melodies, communicating musical ideas, and ultimately unlocking a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of music.
While it may seem daunting at first, learning note names is an achievable goal for anyone willing to invest a little time and effort. With the abundance of resources available – from apps and websites to traditional music books and teachers – the journey of music literacy is more accessible than ever before.
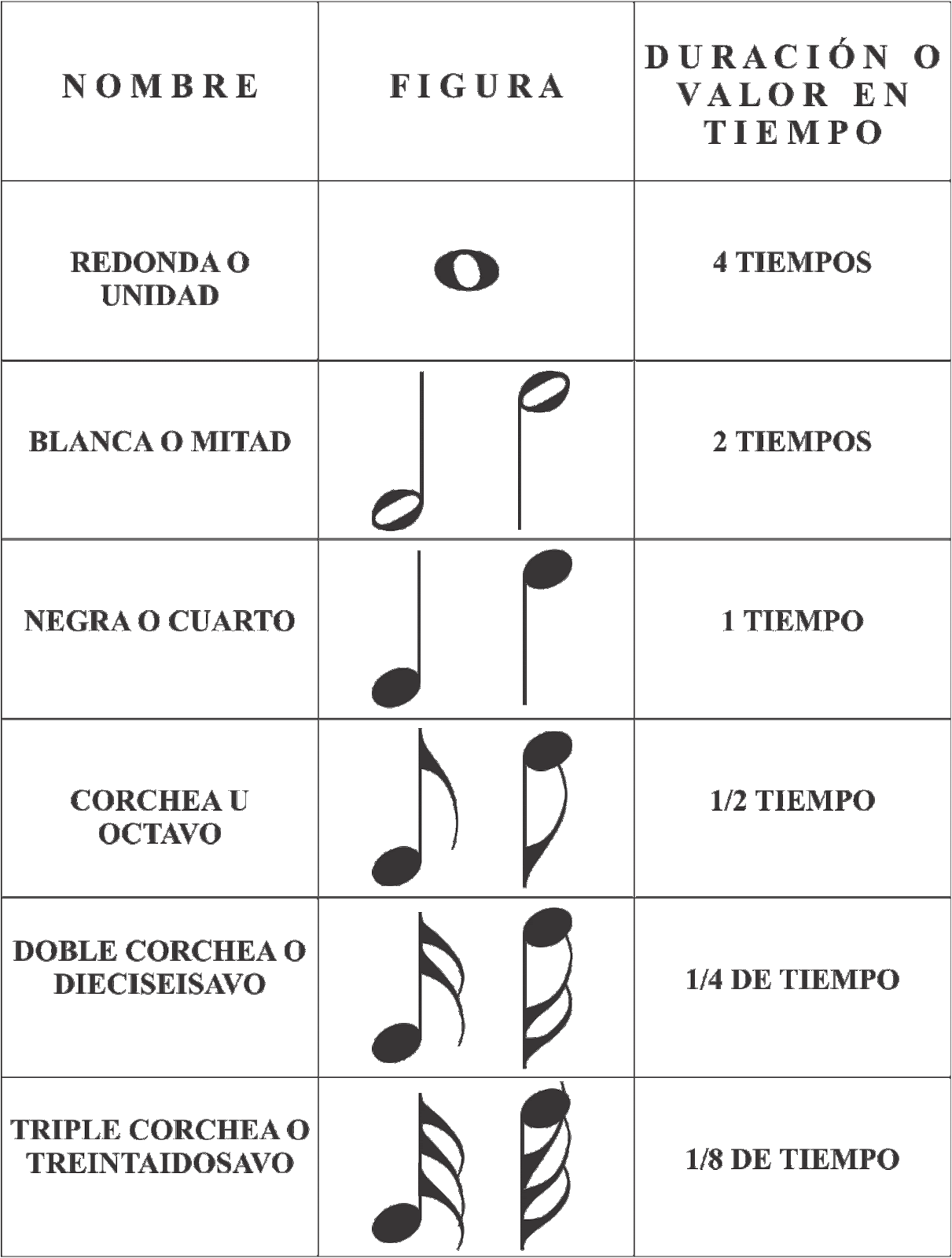
One of the most significant challenges faced when learning note names is memorizing their position on the musical staff. The staff, consisting of five horizontal lines and four spaces, acts as a visual representation of musical pitch. Each line and space corresponds to a specific note, and learning these positions is crucial for reading and understanding sheet music.
To overcome this challenge, many beginners utilize mnemonic devices and visual aids. For instance, the spaces between the lines on the treble clef (the upper clef commonly used for higher-pitched instruments) spell out the word "FACE," providing a helpful memory tool. Similarly, mnemonic sentences like "Every Good Boy Deserves Fudge" are used to remember the lines on the treble clef (EGBDF).
Beyond reading sheet music, understanding note names has numerous benefits. For musicians, it enhances communication and collaboration. Being able to identify a note by its name allows for clear communication of musical ideas and instructions among performers. It also facilitates the process of transcribing music by ear, allowing musicians to learn and share melodies without relying solely on written scores.
For casual listeners, even a basic understanding of note names can enrich the musical experience. Recognizing patterns and intervals between notes enhances melodic awareness and appreciation. It allows listeners to identify recurring themes, analyze harmonies, and develop a deeper understanding of musical structure.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Learning Note Names
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Unlocks music literacy and the ability to read sheet music. | Can be challenging to memorize note positions initially. |
| Facilitates musical communication and collaboration. | Requires consistent practice and effort. |
| Enhances melodic awareness and appreciation. |
While there are numerous advantages to learning note names, it's essential to approach the process with realistic expectations. It requires time, effort, and consistent practice. However, the rewards far outweigh the challenges, paving the way for a richer and more fulfilling musical journey.
Crafting personalized tiktok birthday celebrations with free svgs
Rock the look your guide to 80s girl fashion
Chevy colorado temperature gauge malfunction a deep dive