Unlocking Zone 6 Gardens: A Flourishing Guide to What Thrives
Dreaming of a lush garden bursting with color and life? If you're in USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 6, you're in luck! This temperate zone offers a fantastic range of possibilities for cultivating a stunning outdoor oasis. But knowing precisely what thrives in Zone 6 is key to achieving gardening success. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of Zone 6 gardening, equipping you with the knowledge and inspiration to create your dream garden.
Zone 6 is characterized by average minimum winter temperatures between -10 and 0 degrees Fahrenheit (-23 and -18 degrees Celsius). This moderate climate allows for a longer growing season than colder zones, providing ample opportunity to cultivate a wide variety of plants. From vibrant perennials to delicious vegetables and fruits, Zone 6 gardens can be a haven for both beauty and bounty.
The concept of plant hardiness zones was developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) to guide gardeners in selecting appropriate plants for their specific climate. These zones are based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, dividing North America into 13 zones. Understanding your zone is crucial for avoiding plant damage due to frost and ensuring optimal growth.
Historically, gardeners have relied on local knowledge and experience to determine suitable plants for their region. However, the introduction of the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map revolutionized gardening practices, providing a standardized system for plant selection across the country. This allowed for easier sharing of information and greater success in cultivating diverse plant species.
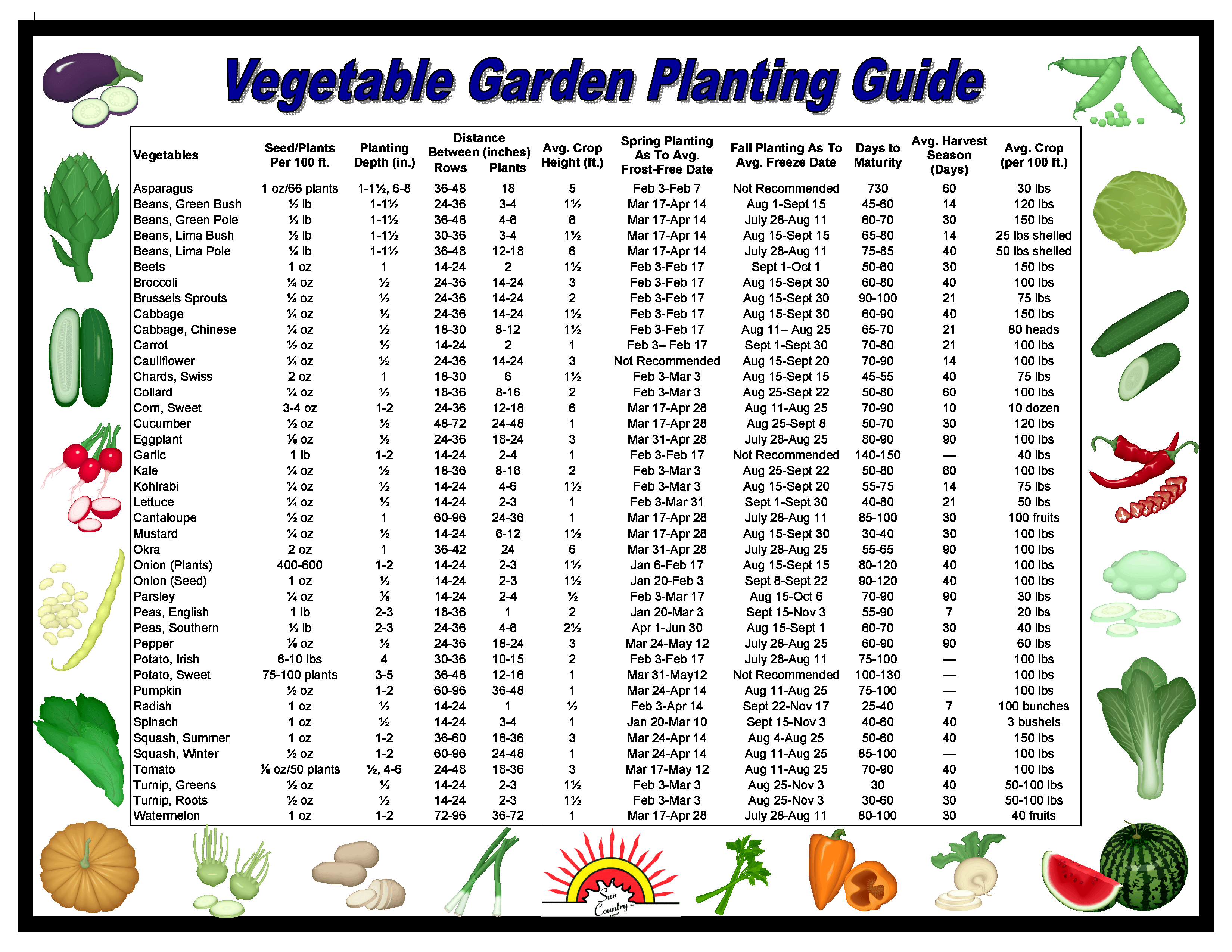
Successfully gardening in Zone 6 relies on choosing plants that are not only cold-hardy but also adapted to the specific conditions of your microclimate. Factors like soil type, sunlight exposure, and rainfall can significantly impact plant growth. Understanding these nuances will empower you to create a thriving garden tailored to your unique environment.
Numerous flowering plants thrive in Zone 6, including coneflowers, hostas, and daylilies. These perennials return year after year, adding splashes of color and attracting pollinators to your garden. For vegetable gardens, popular choices include tomatoes, peppers, beans, and squash. Fruit trees such as apples, cherries, and peaches can also flourish in Zone 6 with proper care.
One of the benefits of gardening in Zone 6 is the extended growing season, allowing for multiple harvests of certain vegetables. Another advantage is the diverse range of plants that can be cultivated, providing opportunities for creating a vibrant and dynamic garden. Furthermore, gardening offers numerous health and well-being benefits, from providing fresh produce to reducing stress and promoting physical activity.
To begin your Zone 6 garden, start by assessing your soil type and amending it as needed. Choose plants that are appropriate for your sun exposure and water requirements. Planting at the right time is also crucial; generally, spring and fall are ideal for planting in Zone 6. Regular watering, fertilization, and pest control are essential for maintaining a healthy and productive garden.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gardening in Zone 6
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Longer growing season | Potential for late frosts in spring and early frosts in fall |
| Wide variety of plants can be grown | Pest and disease pressure can be higher in warmer months |
| Opportunity for multiple harvests | Summer heat can stress some plants |
Best Practices:
1. Soil testing
2. Selecting appropriate plants
3. Proper watering
4. Fertilizing regularly
5. Pest and disease management
Examples of Plants That Grow in Zone 6:
1. Coneflowers
2. Hostas
3. Tomatoes
4. Apples
5. Daylilies
Challenges and Solutions:
1. Late frosts: Use row covers or cold frames to protect young plants.
2. Pests: Implement integrated pest management strategies.
3. Diseases: Choose disease-resistant varieties and practice crop rotation.
4. Summer heat: Provide shade during the hottest part of the day.
5. Drought: Water deeply and less frequently.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is Zone 6?
2. What vegetables grow well in Zone 6?
3. When should I plant in Zone 6?
4. What are the best flowers for Zone 6?
5. How do I protect my plants from frost?
6. What are the common pests in Zone 6?
7. How do I improve my soil?
8. When should I prune my fruit trees?
Tips and Tricks for Zone 6 Gardening: Mulch around plants to conserve moisture and suppress weeds. Consider using raised beds for better drainage and soil control. Practice companion planting to deter pests and improve plant growth.
Gardening in Zone 6 offers a rewarding experience for those seeking to connect with nature and cultivate their own piece of paradise. By understanding the specific needs of plants in this climate and implementing best practices, you can create a thriving garden filled with vibrant blooms, delicious produce, and the tranquility of nature. Embracing the challenges and joys of Zone 6 gardening will empower you to cultivate not only a beautiful landscape but also a deeper appreciation for the natural world. So, gather your tools, select your favorite plants, and embark on this fulfilling journey of creating your dream Zone 6 garden! Don't hesitate to explore additional resources like local nurseries, gardening books, and online forums for further inspiration and guidance. Happy gardening!
Decoding paint color matching a deep dive into hues
Sauk county police reports unveiled
How to put on a gas mask your guide to safety and preparedness


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/burningbush-5a7f7d343128340036d79b96.jpg)